It is no exaggeration that Xian is the first choice if you are willing to find the longest history of China. This region is one of the vital birthplaces of the profound Chinese civilization. Benefiting from the fertile land and comfortable climate in ancient time, the rulers of 13 dynasties have set up their capitals in Xian successively. Thus, Xian is one of the cities which preserve a wealth of historical heritages in China.
Prehistory The Lantian Man, which was found in Lantian County of Xian, has inhabited in this land about 800,000 years ago. The founded skulls fossils is said to be the earliest and best preserved ones in China until now. Coming to 300,000-400,000 years ago, the primitive people around Xian have turned into the stage of primitive clan communes gradually. The base of this region’s agricultural production should be started when the Banpo Man made living here about 6,000 years ago. They have settled down in the eastern suburban of Xian City, setting up the Matriarchal clan villages.
In the Slave SocietyThe slave society of China mainly refers to the periods of the Xia (21st-16th century BC), Shang (16th-11th century BC), Western Zhou (11th century BC-771BC) as well as Spring and Autumn Peroid (770 BC-476). During this long history, more and more nations have immigrated to the Guanzhong Plain the center of which is just current Xian. Therefore, both of this region's economy and political system has gained rapid development. Until to the Western Zhou Dynasty, the Wenwang have moved the capital-Fengjing to the west bank of the Fenghe River nearby Xian. It played as the dynasty's religious and cultural center. Later, his heir Wuwang built the political center on the east bank of the Fenghe River, namely, Haojing. This should be the first recorded dynasty founded the capital in Xian City.
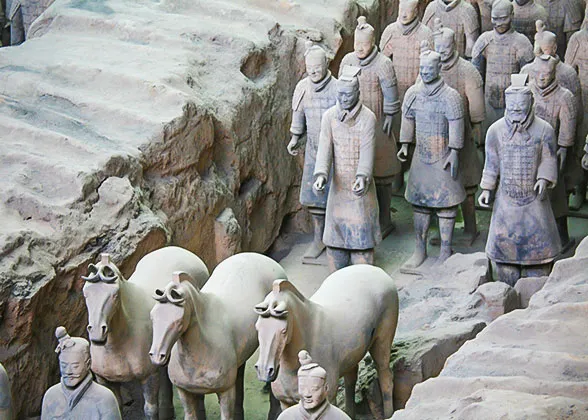
In the Warring State Period (476BC-221BC) and the Qin Dynasty (221 BC-206 BC)Coming to the end of the Eastern Zhou Dynasty, namely, the Warring States Period, there mainly distributed seven powerful states in China. Qin, one of the seven states, was located in the center of Shaanxi Province and east Gansu Province. Later, Ying Zheng, Emperor Qin Shi Huang, set up the first feudal dynasty in Xianyang (consists of current Xian and Xianyang cites) after unifying the other six states. Although this dynasty fallen soon, a great number of historical relics were left, for example, the so famous Terra-cotta Warriors and Horses. Until now, some traditions and cuisines from the Qin Dynasty are still kept by the Xian locals.
In the Han Dynasty (206 BC-220)The Western Han Dynasty (206 BC-24AD), which is the third dynasty setting up its capital in Xian, constructed its capital -Chang'an on the relics of the Qin's Xianyang. Once, Chang'an City was the largest one in the world, covering an area of about 36 square kilometers (13.9 square miles). Now, the site of the Weiyang Palace is preserved well in Xian. The famous 'Silk Road' which starts from the Chang'an City appeared during the period of Wudi, opening the communication between China and overseas countries. On the other hand, the emperors carried out a series of policies to help the rehabilitation of the people. The Chang'an became a thriving city both in economy and polity in the world wide.
In the Sui (581-618) and Tang (618-907) DynastiesAt the found of the Sui Dynasty, the Han's Chang'an City has been destroyed seriously owing to long years of wars from 220 to 589. Therefore, the emperor built a new city just to southeast of the old Chang'an City, called Daxing City. After the Tang Dynasty overthrew the Sui and captured the Daxing City, the first emperor of Tang renamed the city as Chang'an City again. Later, some subsequent construct and renovation projects were taken. In the early period of Emperor Taizong, the Daming Palace was constructed, which was the political center of the whole dynasty later. There is no doubt that Tang should be the most prosperous dynasty in Chinese history. Thus, as the center, Chang'an was one of the largest economical, political and cultural centers in the world at that time. Most overseas travelers and businessmen came to Chang'an, enjoying the city's gloss.
On the other hand, the Buddhism also expanded rapidly in Chang'an with the support of the governors. Now, the existing Big Wild Goose Pagoda should be the outstanding representation of the Buddhist building in Xian. Additionally, the prosperous and peaceful city attracts a great number of artist and poets, inspiring them to create so many masterpieces throughout the ages. In fact, the Tang culture has influenced this region deeply, spanning from architectural style to food, even to the city's soul.
In the Ming Dynasty (1368-1644)From the end of the Tang Dynasty, the Chang'an City has lost its top position gradually; however, it was still one of the vital prefectures in the later dynasties. In 1369 of the Ming Dynasty, Xian gained its current name officially. From the next year, the current Xian City Wall has been constructed.
The Summary of the Modern HistoryOctober 22, 1911---the local revolutionists pulled down the governance of the Qing Dynasty in Xian.
1925---the national army led by Dr. Sun Yat-sun overthrew the reactionary warlord in Xian.
1927---some members of the Chinese Communist Party launched a military school in Xian, training a number of revolutionists.
December 12, 1936---Zhang Xueliang and Yang Hucheng captured the Generalissimo Chiang Kai Shek by initiating a military exhortation, namely, the Xian Incident. The incident spurred the Kuomintang to unify the Communist for resisting the Japanese invaders.
May 20, 1949---Xian City was liberated by the Chinese People's Liberation Army.
May 25, 1949—The People's Government of Xian City was launched.
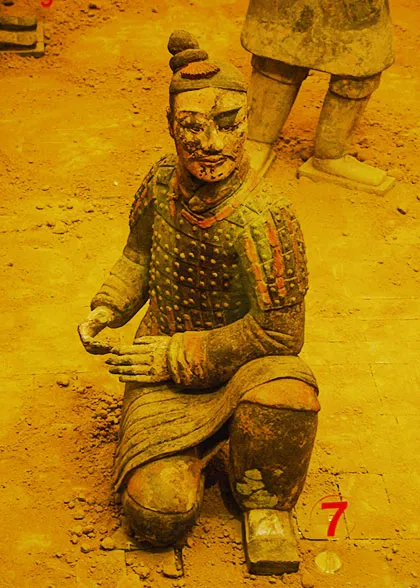 The Terra Cotta Pit No. 2 is 20 meters due east of Pit No. 1. It is 6,000 square meters subdivided into L-Shaped foursquare sections, where archeologists unearthed 1,000 warriors, 500 horses, and 89 wooden chariots. The horses are both for pulling chariots and for carrying riders. It reflects a vibrant and dynamic atmosphere.
The Terra Cotta Pit No. 2 is 20 meters due east of Pit No. 1. It is 6,000 square meters subdivided into L-Shaped foursquare sections, where archeologists unearthed 1,000 warriors, 500 horses, and 89 wooden chariots. The horses are both for pulling chariots and for carrying riders. It reflects a vibrant and dynamic atmosphere.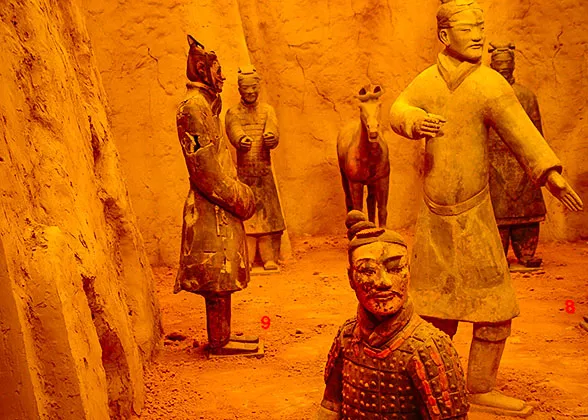

![]() Related Links:
Related Links:.jpg)
 Set of figures in Pit No. 1 includes: Large body of troops from the left wing marshalled in battle order.
Set of figures in Pit No. 1 includes: Large body of troops from the left wing marshalled in battle order.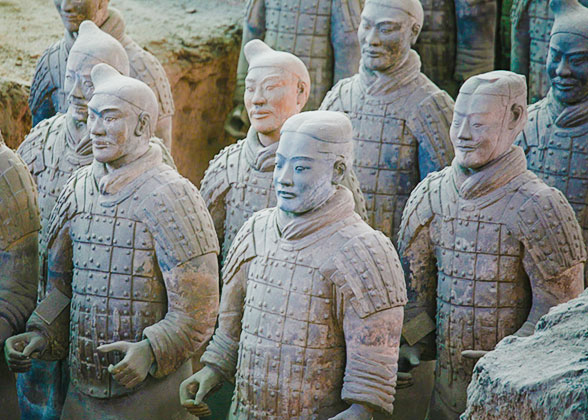
 Museum of Qin Terra Cotta Warriors and Horses:
Museum of Qin Terra Cotta Warriors and Horses: 1974. It caught the attention of archeologists immediately. They came to Xian in droves to study and to extend the digs. They had established beyond doubt that these artifacts were associated with the Qin Dynasty (211-206 BC).
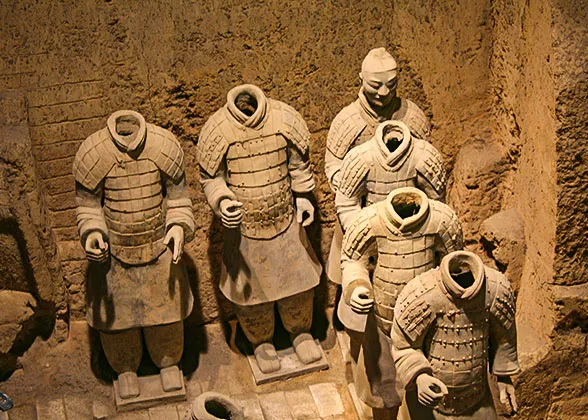
1974. It caught the attention of archeologists immediately. They came to Xian in droves to study and to extend the digs. They had established beyond doubt that these artifacts were associated with the Qin Dynasty (211-206 BC). three sections: No. 1 Pit, No. 2 Pit, and No. 3 Pit respectively. They were tagged in the order of their discoveries. No. 1 Pit is the largest, first opened to the public on China's National Day, 1979. There are columns of soldiers at the front, followed by war chariots at the back.
three sections: No. 1 Pit, No. 2 Pit, and No. 3 Pit respectively. They were tagged in the order of their discoveries. No. 1 Pit is the largest, first opened to the public on China's National Day, 1979. There are columns of soldiers at the front, followed by war chariots at the back. Foremost is the China's greatest archeological excavation, the
Foremost is the China's greatest archeological excavation, the Housing more than 2,300 famous steles and inscribed memorial tablets of the Han, Wei, Sui, Tang, Yuan, Ming, Qing dynasties and known as the largest 'stone-book warehouse’ in China, the
Housing more than 2,300 famous steles and inscribed memorial tablets of the Han, Wei, Sui, Tang, Yuan, Ming, Qing dynasties and known as the largest 'stone-book warehouse’ in China, the Additional attractions are the
Additional attractions are the
 The cultural and historical significance of Xian, as well as the abundant relics and sites, help Shaanxi enjoy the laudatory title of 'Natural History Museum'. The
The cultural and historical significance of Xian, as well as the abundant relics and sites, help Shaanxi enjoy the laudatory title of 'Natural History Museum'. The  As tourist development grows in Xian, the hotel industry flourishes more and more. It is very easy to find a hotel in Xian, ranging from 5 star hotels to youth hostels. Of course, it will be any traveler's first choice to stay in the city center due to the superior geographical location and the convenient transportation.
As tourist development grows in Xian, the hotel industry flourishes more and more. It is very easy to find a hotel in Xian, ranging from 5 star hotels to youth hostels. Of course, it will be any traveler's first choice to stay in the city center due to the superior geographical location and the convenient transportation.

